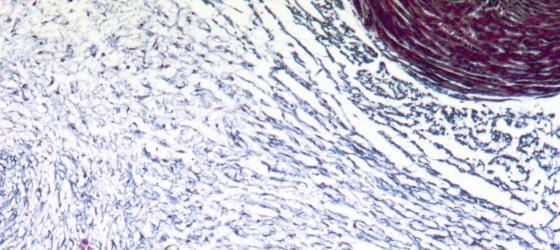
This tissue lacks fibers and originates during embryonic development. It is still present in adults and can be found in the dental pulp and vitreous body. Hydrophilic extracellular matrix represents its main component and it provides the tissue with a jelly texture. It can also be found in the umbilical cord as Wharton’s jelly.
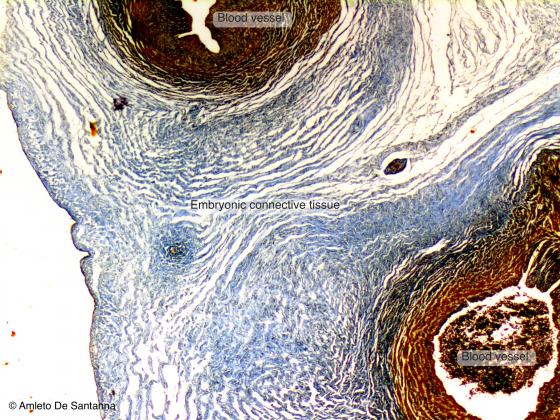
Figure C2. Human umbilical cord. The mucous connective tissue is found in the umbilical cord (Wharton’s jelly - substantia gelatinea funiculi umbilicalis). In this type of connective tissue, fibers are sinked into a soft gelatinous material in order to be elastic and flexible and to allow the passage of cells such as macrophages and lymphocytes. The characteristics of its structure allow a certain degree of compression and deformation of the organ without affecting the blood flow to the fetus and the fast return to its original shape. Ignesti X25
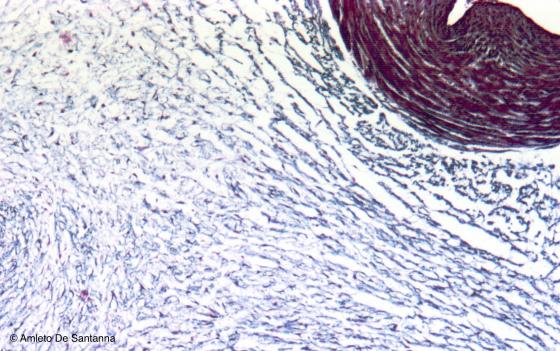
Figure C3. Human umbilical cord. Wharton’s jelly at higher magnification. Mallory-Azan X64